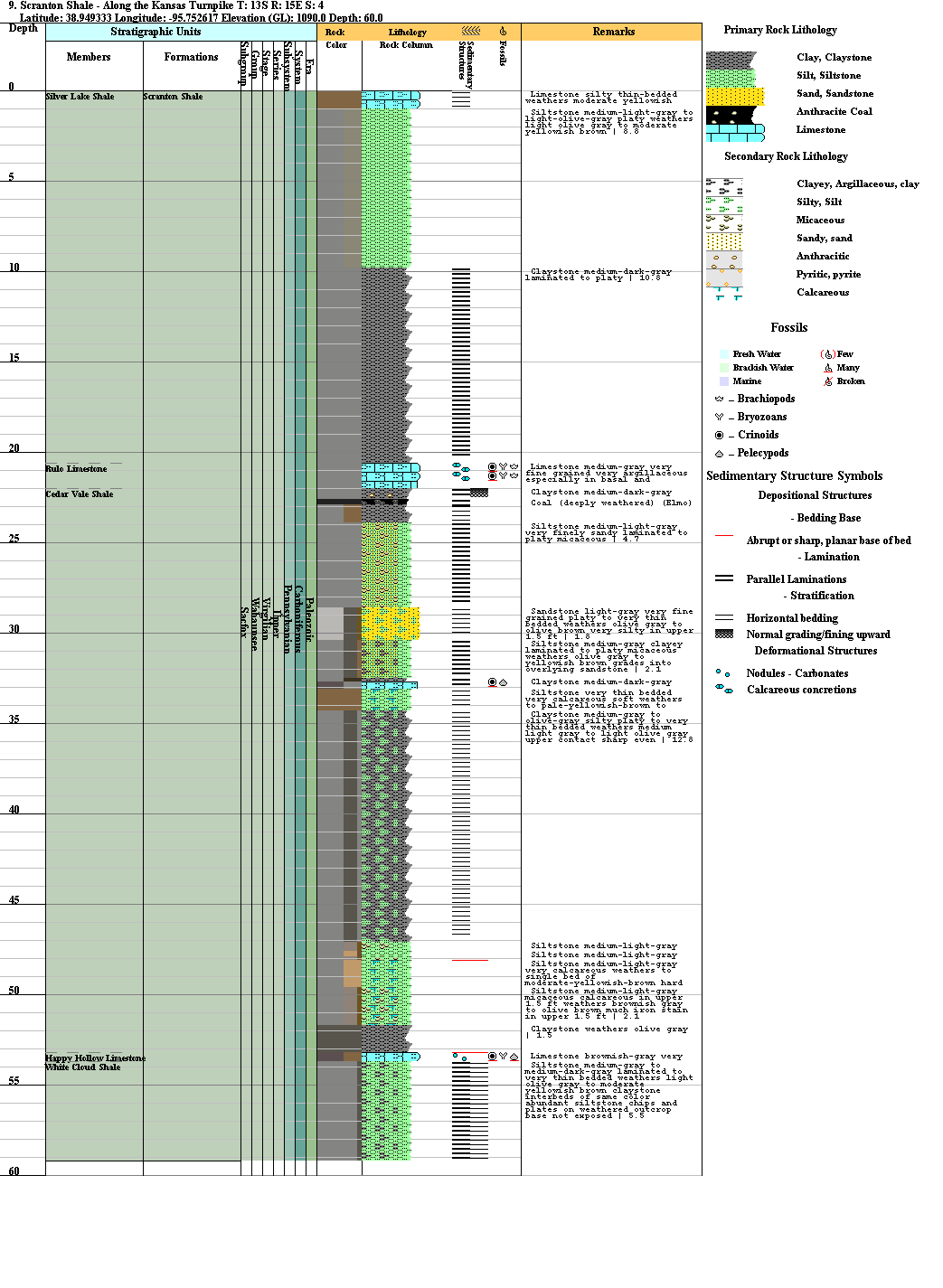
Planar Lamination In Stratigraphic Column

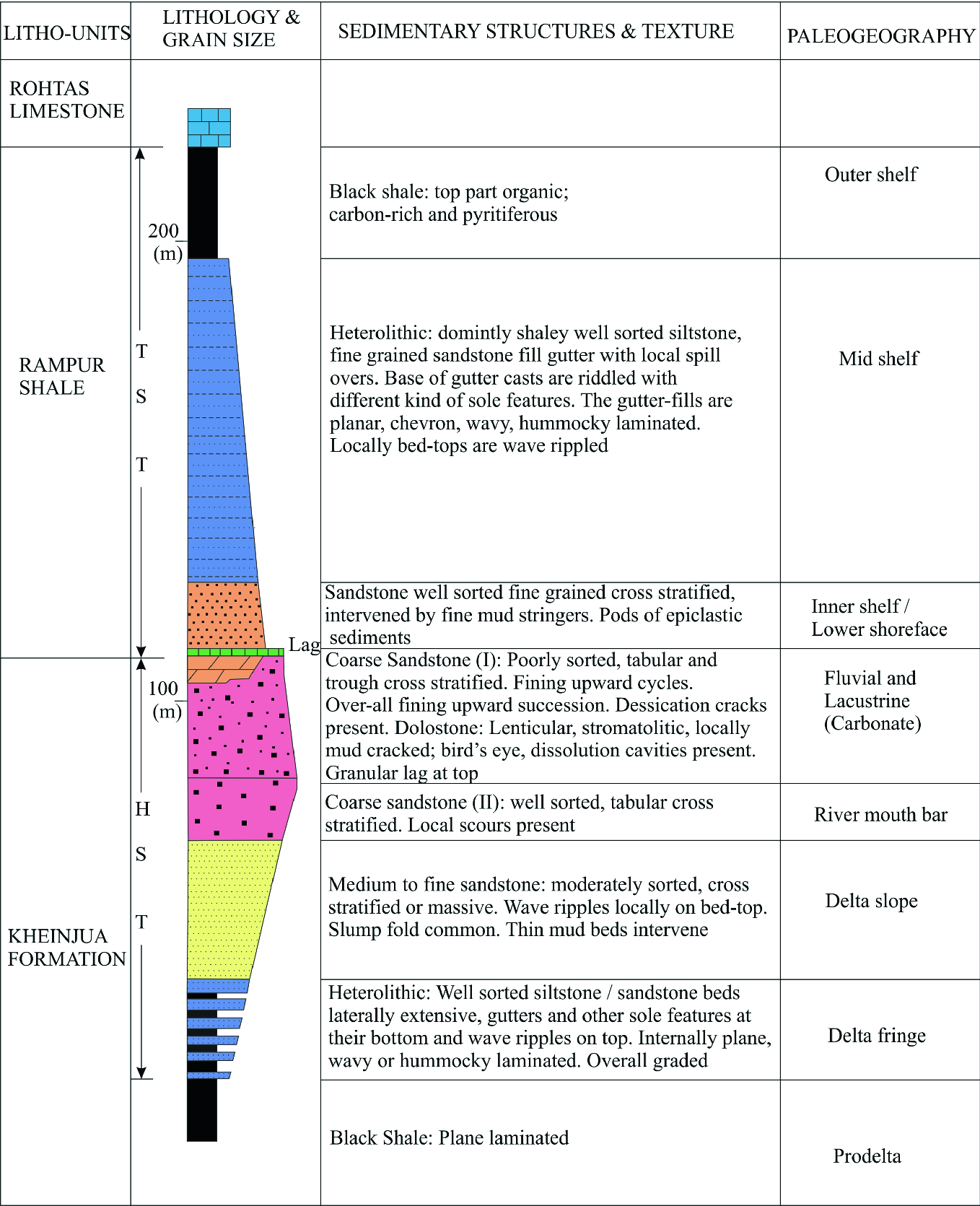
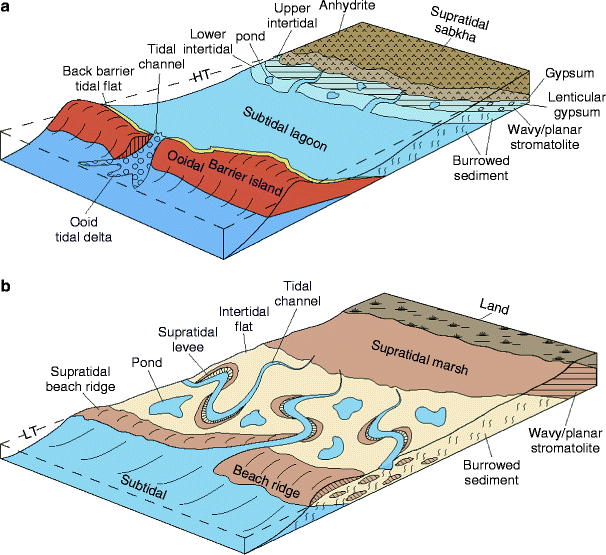
Distal facies display repetitive successive units that rarely exceed two meters in thickness whereas proximal facies often include units of 20 m or more.
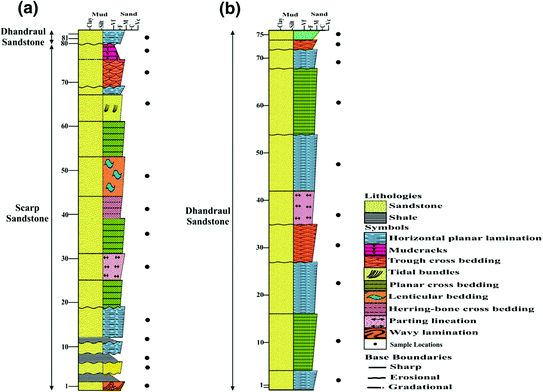
Planar lamination in stratigraphic column. Here is an outline of how to approach interpreting the depositional environment represented by a stratigraphic column. Cross stratification angles vary from 0 to 20 fig. Look for sedimentary structures that are characteristic of a specific environment or process. The planar laminated to low angle cross stratified facies typically shows fine lamination that is geometrically arranged in bed sets having horizontal to low angle cross stratification.
Generalized stratigraphic column of the husky creek fm. The sedimentary structures which result are roughly horizontal units composed of inclined layers. In geology cross bedding also known as cross stratification is layering within a stratum and at an angle to the main bedding plane. Most sandstone beds are medium grained and display planar lamination with well developed parting lineations large scale hummocky cross stratification like structures hcs.
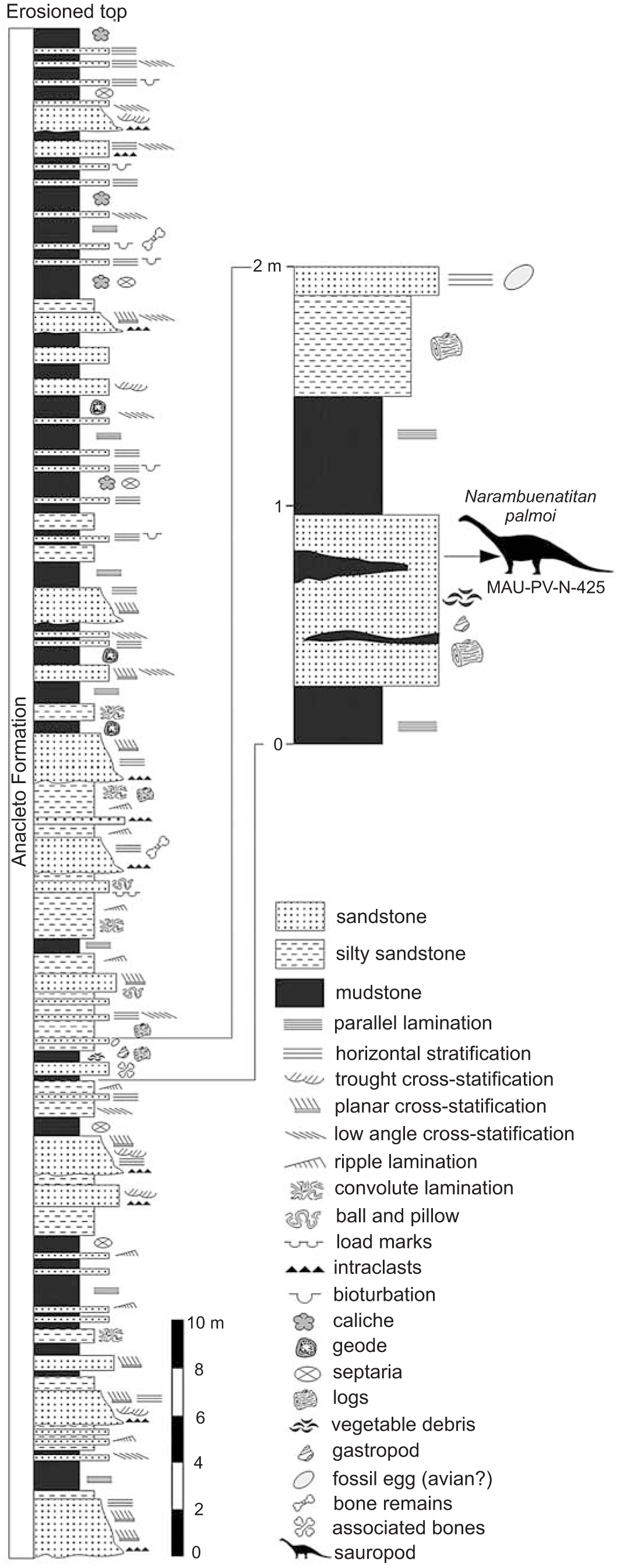
Planar lamination step 4. Primary structures include planar lamination and sporadic small scale cross lamination. Which displays a faint planar lamination disrupted by polygonal fractures. 6c and symmetrical to slightly asymmetrical ripple bedforms and cross lamination.
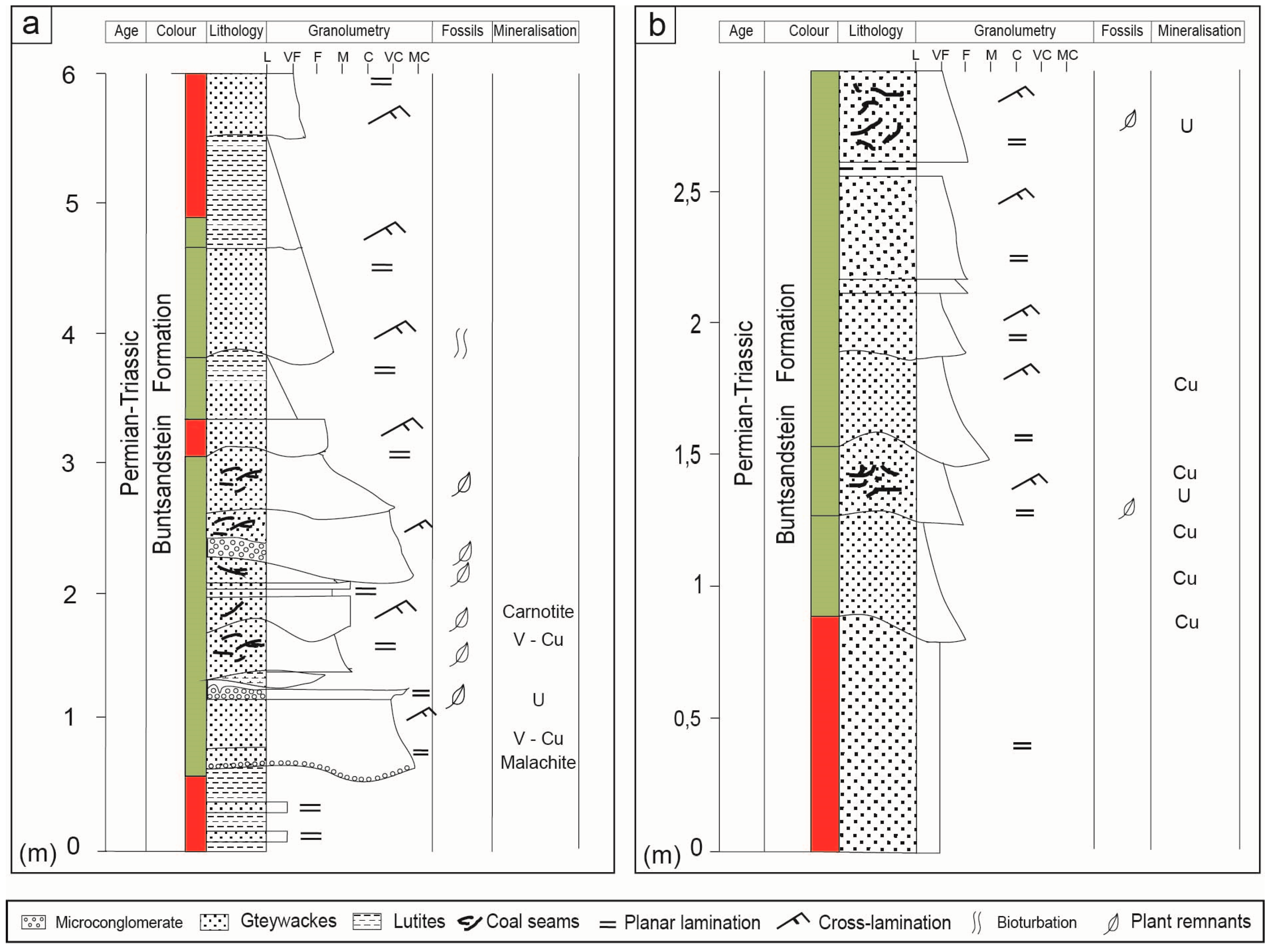
The hcs like structures are composed of stacked lamina sets that thin and thicken within each bedset with successive lamina sets separated by muddy partings. Evaluate how the vertical sequence of sedimentary structures changes to refine or correct your environmental interpretations. If you hypothesized that set of a fining upward sandstones were turbidites which have planar lamination and current ripple cross lamination but there is also trough cross stratification in a number of the beds ask yourself if there is a way for trough cross stratification to form in turbidites. When developed some slightly curved or planar lamination foresets may be observed with no evidence of clear grain size sorting.
Bed thickness is highly variable. As the river migrates towards the direction of the eroding bank the current ripples of the point bar will end up being deposited on top of planar lamination dune cross stratification of the bank. The coarser grained areas that result from a faster flow speed will have upper planar lamination or dune cross stratification. Turbidites vs river channel deposits.
Planar lamination step 4. 4 a shows a large scale planar lamination partially cut by the drill core. These laminations can be related to solitary or stacked trough crossbeds st or planar crossbeds sp fig. The original depositional layering is tilted such tilting not being the result of post depositional deformation cross beds or sets are the groups of inclined.
Interpreting stratigraphic columns step 1. The point bar of the river will produce current ripple lamination due to the finer sediment and slower flow speeds.